In August 2024, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared an emergency of a global scale due to the rapid spread of a new monkey smallpox that arose in the Congo and spread to other countries in Africa. The outbreak has already covered Burundi, Kenya, Rwanda and Uganda, which caused serious concern for the international community.
A new strain known as Clade 1B is a mutation of a virus and a cola, which was previously considered less dangerous. However, the current variant is noted for high rates of spread and increased mortality, especially among children and pregnant women. WHO has already warned the Member States about the need to prepare for the possible global spread of this virus, which includes vaccination measures and other precautions.
Professor Land Lang from the University of Oxford expressed serious anxiety about the current situation, calling it "incredibly disturbing". He also noted that the monkey smallpox virus can be the most dangerous infection of the present because of its ability to spread rapidly and cause serious complications.
Comparison with the flash of 2022
The outbreak of monkey smallpox, which occurred in 2022, was caused by the II Clay of the virus, which had a relatively low mortality rate. At that time, the virus spread mainly to men who had sexual contact with other men and was localized in Europe and the United States. However, at that time it was possible to restrain the outbreak due to active vaccination and appropriate measures.
However, the situation in 2024 is much more complicated due to the mutation of the virus and its spread in regions with restricted medical services. According to the African Disease Control and Disease Centers, more than 14.5 thousand cases of infection and more than 450 deaths were registered in the first half of 2024, which is a significant increase compared to the previous year.
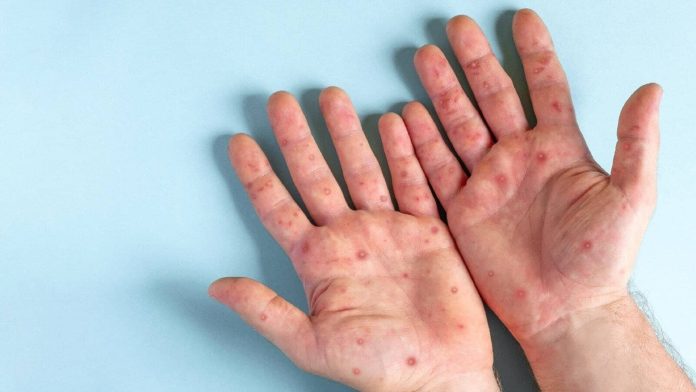
The main symptoms of monkey smallpox are rash, fever, headache, muscle pain, general weakness and enlargement of the lymph nodes. In some cases, the development of proctitis, inflammation of the parotid gland (mumps) and damage to other organs, which can lead to serious complications and even death, especially in people with weakened immunity, children and pregnant women.
Prevention and vaccination
WHO recommends limiting vaccination only at risk groups, including health workers, pregnant women and persons with weakened immunity. Three smallpox vaccines, including Jynneos, ACAM2000 and Orthopoxvac, which were used during previous outbreaks, are available. However, mass vaccination is not recommended because of limited data on the effectiveness of these vaccines against a new strain.