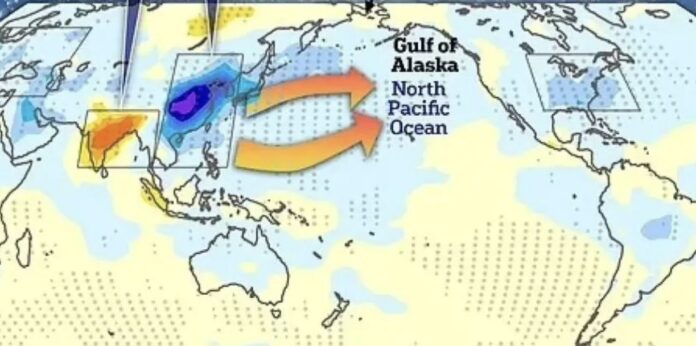
A new study confirms that China can affect global warming without even intending to do so. The team of scientists from China's Oceanic University found that from 2010 to 2020, China created "thermal clots" over the northeastern part of the Pacific. This led to a temperature rise in the Bering Strait and at a distance of about 1600 kilometers to the Alaska Bay. The negative effects include mass extinction of fish, the spread of toxic algae and the disappearance of whales.
Researchers have found that this warming is due to a partial reduction in China's aerosol emissions. Aerosols play a dual role: they pollute the environment, but also reflect the solar heat that goes back into space, which leads to cooling of the Earth. As a result, scientists urge the Chinese government to revise their policies on aerosols, as their ban can lead to a further increase in temperature in the region and threats to life in the oceans.
The study shows that in recent decades, China has encountered record waves of heat, for example, in 2015, the temperature reached 51.6 degrees Celsius. After successful reduction of aerosol emissions in 2010, there is a change in the nature of these waves of heat.
During the study, scientists have developed 12 computer climate models that were used with two scenarios:
- Emissions in East Asia remained stable.
- Emissions in East Asia have decreased over the last decade.
The results showed that in models where the number of emissions did not change, the temperature in other regions remained stable. However, reducing the amount of emissions has led to an increase in temperature in the northeastern regions of the Pacific.
Clean air without aerosols means that less heat is reflected back into space. This leads to an increase in surface temperature, which in turn leads to the formation of high pressure systems. These systems, formed above the planet's atmosphere, have made low pressure systems in the Pacific more intense. This has led to an expansion of the Aleutian minimum, which transports the warm air to the northeast of the Pacific Ocean, and the weakening of the winds, which usually cool the surface of the ocean. The result is more hot conditions.
The study also indicates that the restriction of aerosol emissions really contributes to global warming. However, their increase leads to the premature death of eight million people annually worldwide, according to NASA.